14
2024-11
China launches ocean-salinity detection satellite
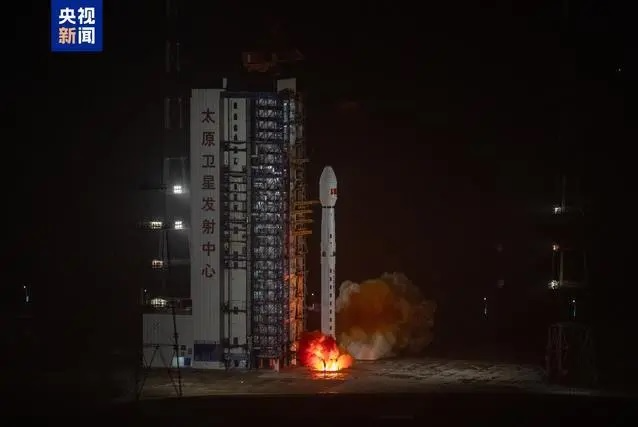

A Long March 4B Y53 carrier rocket carrying a new satellite for ocean-salinity detection blasts off from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center in North China's Shanxi province on Nov 14, 2024. [Photo/CCTV]
TAIYUAN -- China sent a new satellite for ocean-salinity detection into space on Thursday from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center in north China's Shanxi Province, according to the China National Space Administration (CNSA).
The satellite was launched at 6:42 am (Beijing Time) using a Long March-4B Y53 carrier rocket, and has successfully entered its preset orbit.
The satellite will fill the gap of China's high-precision global ocean-salinity detection capabilities, improve data collection on ocean dynamics and environmental factors, and boost the accuracy of China's marine forecasting products, said the CNSA.
It will also support marine environmental forecasting, ecological forecasting, water-cycle monitoring, short-term climate prediction, and global climate change research, providing critical data for applications in agriculture, disaster mitigation, meteorology and other related industries, according to the CNSA.
It was the 545th flight mission of the Long March series rockets.
-
29
2025-05

Tianwen-2 Mission Launched Successfully
At 1:31 AM today, China successfully launched the Tianwen-2 planetary exploration probe from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center using the Long March-3B Y110 carrier rocket.
-
13
2025-05
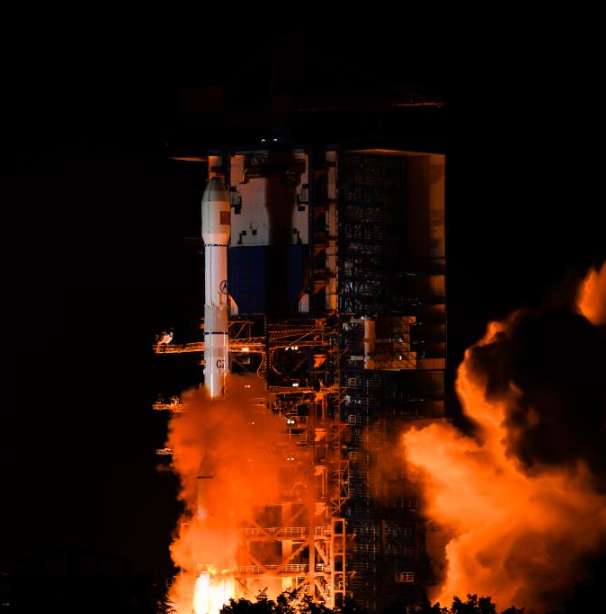

Communication Technology Experiment Satellite No. 19 Successfully Launched
At 2:09 on May 13, China successfully launched the Communication Technology Experiment Satellite No. 19 from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center using a Long March 3B carrier rocket. The satellite smoothly entered its predetermined orbit, and the launch mission was a complete success.
-
12
2025-05
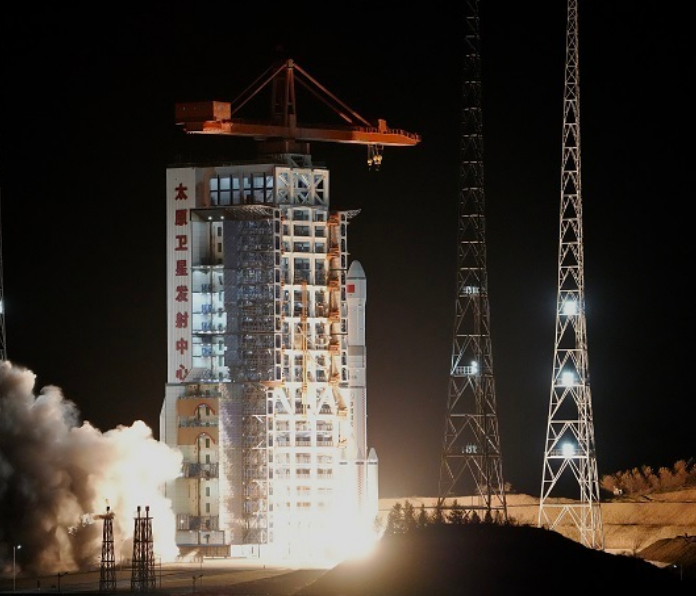

Remote Sensing Satellite No. 40, Group 02, Successfully Launched
On May 11 at 21:27, China successfully launched the Remote Sensing Satellite No. 40, Group 02, from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center using a Long March 6A carrier rocket. The satellite entered its predetermined orbit smoothly, and the launch mission was a complete success.